Mastering the Digital Data Lifecycle: Why It Matters Now More Than Ever
July 1, 2025
In a world where information is currency and data volumes grow at exponential rates; unmanaged data is a liability.
When governed effectively, data transforms into a strategic asset. Shared information not only makes stakeholders happy, but it can also drive innovation, improve efficiency, and reduce risk.
At Informed Byte, we believe that managing data isn't just a technical necessity—it's a foundational practice for sustainable, intelligent operations. This article will guide you through what the digital data lifecycle really means, why it's essential, and how your organisation can master it.
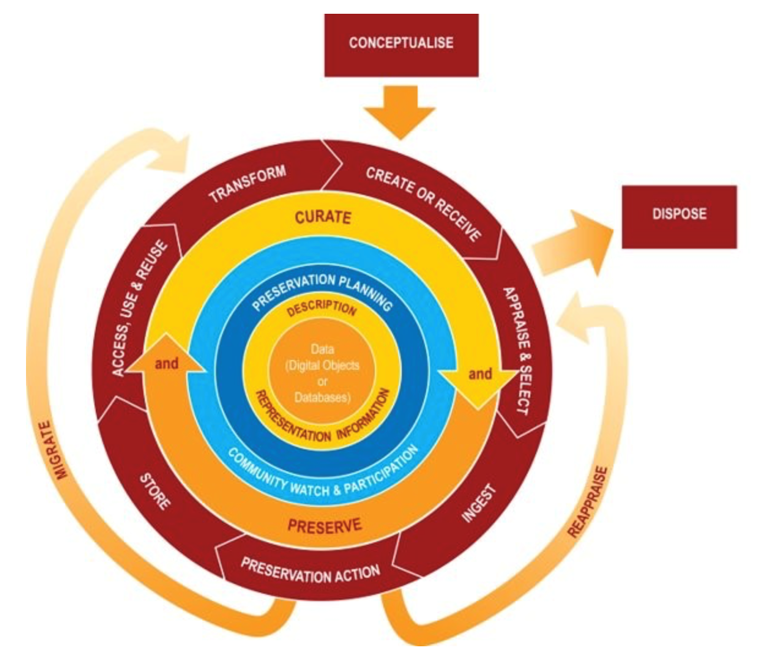
Digital Curation Centre
What Is Digital Data Lifecycle Management?
DDLM is the governance framework that manages data from the moment it's created or acquired to its final disposal. Just like a physical product has a lifecycle—from design and manufacturing to sale and end-of-life—so does data.
Typically, this lifecycle comprises several stages:
Creation or Capture
Storage
Usage
Sharing or Distribution
Archiving
Disposal or Deletion
Each stage comes with its own technical requirements, compliance obligations, and opportunities for optimisation. But the real power lies in integrating these stages into a cohesive, strategic system.
Why Lifecycle Management Is No Longer Optional
Organisations used to be able to “set and forget” their data practices—stash it in a shared drive and hope for the best. Those days are over. Today, the sheer volume, velocity, and variety of data make such practices not only inefficient but risky.
Regulatory Compliance
Data privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations (e.g., HIPAA, FINRA) require clear oversight of data usage and retention.
Operational Efficiency
Old, unused, or redundant data clogs systems and slows down search and retrieval processes.
Cybersecurity
Data is most vulnerable when it's poorly tracked.
Cost Management
Storing all data indefinitely is expensive.
Data Quality and Decision-Making
Dirty data leads to bad decisions.
A Closer Look at Each Stage
Let's dive deeper into each phase of the data lifecycle—and what good management looks like at each point.
Creation or Capture
Data enters your organisation in many ways: forms, emails, apps, sensors, customer interactions.
Storage
Where and how your data is stored impacts everything—from accessibility to security to compliance.
Usage
This is the value-extraction stage: data is consulted, processed, shared, and integrated into operations, dashboards, and decisions.
Sharing and Distribution
Whether it's internal collaboration or external sharing, data is constantly being transferred.
Archiving
Not all data needs to be immediately available. Some may need to be retained for regulatory, historical, or strategic reasons—but rarely accessed.
Disposal or Deletion
When data has reached the end of its usefulness or retention period, it must be properly deleted.
Technology's Role in DDLM
Managing a data lifecycle manually is nearly impossible in modern enterprises. That's where technology—especially metadata-driven automation—plays a critical role.
Embedding a Culture of Data Stewardship
Technology is only half the story. For DDLM to work, your organisation must buy into it.
Common Challenges (and How to Overcome Them)
Even with the best intentions, organisations face roadblocks.
Where to Start?
If you're just beginning your DDLM journey, don't aim for perfection from day one.
Final Thoughts: Data as a Living Asset
We often say that data isn't a one-time event—it's a living asset. It grows, evolves, ages, and eventually becomes obsolete.
Your data lifecycle starts here